Introduction:
Aluminum foundries play a crucial role in the manufacturing sector, contributing to the country’s industrial growth and economic development. In this article, we will explore the landscape of aluminum foundries, highlighting their significance and discussing the role of alumina ceramic foam filters in the production process.
The Growing Aluminum Industry:
Significant expansion of its aluminum industry in recent years. Several factors contribute to this growth, including:
a. Proximity to Raw Materials: Geographical location provides easy access to bauxite, the primary ore used to produce aluminum.
b. Skilled Labor Force: The workforce is skilled in metalworking and foundry operations, making it an attractive destination for aluminum manufacturers.
Key Players in the Aluminum Foundry Sector:
Several prominent companies are operating aluminum foundries. These include:
a. Nemak: A global leader in aluminum components for the automotive industry, Nemak has multiple plants, producing cylinder heads, engine blocks, and other components.
b. Met-Mex Peñoles: This subsidiary of Grupo Bal specializes in aluminum smelting and production, contributing significantly to aluminum output.
c. Rassini: Although primarily known for brake and suspension components, Rassini also manufactures aluminum parts for various industries.
Alumina Ceramic Foam Filters in Aluminum Foundries:
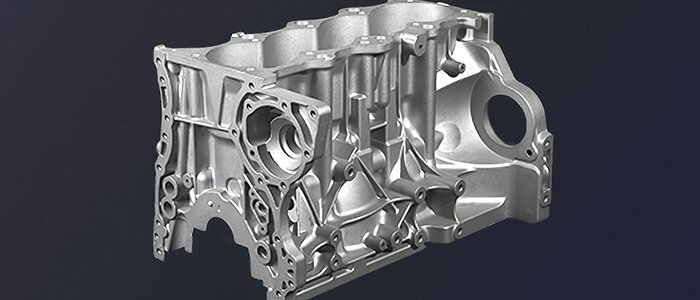
Alumina ceramic foam filters are essential components in the aluminum casting process. These filters are made from high-purity alumina ceramics and have a highly porous structure. Here’s how they contribute to the foundry process:
a. Filtration: Alumina ceramic foam filters remove impurities and non-metallic inclusions from molten aluminum, ensuring the final product meets quality standards.
b. Temperature Control: These filters help regulate the temperature of the molten metal as it flows into molds, preventing defects like porosity.
c. Improved Casting Quality: By enhancing metal cleanliness and reducing turbulence during pouring, alumina ceramic foam filters result in higher-quality castings.
d. Cost Savings: The use of these filters can lead to reduced scrap rates and lower production costs in the long run.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations:
Aluminum foundries are increasingly adopting environmentally friendly practices. This includes recycling aluminum scrap and implementing energy-efficient technologies. Alumina ceramic foam filters also play a role in sustainability by improving casting quality, reducing material waste, and enhancing energy efficiency.
Certainly, let’s continue with the article on aluminum foundries, focusing on sustainability practices, challenges faced by the industry, and the future outlook.
Sustainability Practices in Aluminum Foundries:
Sustainability has become a key focus for the aluminum foundry industry. Here are some of the sustainable practices being adopted:
a. Recycling: Foundries are increasingly recycling aluminum scrap, reducing the demand for primary aluminum production and minimizing waste.
b. Energy Efficiency: The industry is investing in energy-efficient technologies to reduce its carbon footprint. This includes using cleaner energy sources and optimizing manufacturing processes.
c. Emissions Control: Emission control measures are being implemented to minimize air and water pollution, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
d. Circular Economy: Some foundries are exploring circular economy principles by reusing and repurposing materials, thereby reducing the overall environmental impact of production.
Challenges Faced by the Aluminum Foundry Industry:
Despite its growth, the aluminum foundry sector faces several challenges:
a. Global Competition: Competition from other aluminum-producing nations poses a challenge. Foundries must continually innovate to remain competitive in the global market.
b. Energy Costs: Fluctuating energy costs can impact the profitability of aluminum production. Finding cost-effective and sustainable energy solutions is a priority.
c. Environmental Regulations: Compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations can be costly and challenging for foundries. Balancing sustainability with economic viability is essential.
d. Supply Chain Disruptions: Like many industries, the aluminum foundry sector is susceptible to supply chain disruptions, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic. Managing these disruptions is critical for continuity.
The Future Outlook for Aluminum Foundries:
The future of the aluminum foundry industry appears promising, but it will require adaptability and innovation. Here are some key considerations for the industry’s future:
a. Technological Advancements: Embracing advanced technologies like automation, artificial intelligence, and 3D printing can enhance efficiency and competitiveness.
b. Sustainable Growth: Continued focus on sustainable practices and environmental responsibility will be essential for long-term success.
c. Diversification: Expanding into new markets and diversifying product offerings can mitigate risks associated with global economic fluctuations.
d. Collaboration: Collaboration with research institutions and government agencies can drive innovation and address industry-specific challenges.
e. Global Demand: The demand for aluminum products, especially in the automotive and aerospace sectors, is expected to grow. Foundries can leverage this demand by maintaining high quality and reliability.
f. Workforce Development: Investing in workforce development and training programs will ensure a skilled labor force capable of meeting industry demands.
The Role of Aluminum Foundries in Key Sectors:
Aluminum foundries serve a diverse range of sectors, each with its unique demands and requirements. Here are some of the key sectors where the industry plays a vital role:
a. Automotive Industry: Aluminum foundries are integral to the automotive sector, producing engine components, transmission parts, and lightweight structures that contribute to fuel efficiency.
b. Aerospace Industry: With the aerospace industry’s growing presence, foundries supply critical parts such as aircraft engine components, landing gear, and structural elements.
c. Construction and Infrastructure: Aluminum foundries provide materials for the construction industry, including extrusions, architectural elements, and specialized components.
d. Electrical and Electronics: The sector relies on aluminum for heat sinks, connectors, and casings due to its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
e. Consumer Goods: Aluminum foundries also contribute to the production of consumer goods like cookware, home appliances, and electronics.
f. Renewable Energy: With an increasing focus on renewable energy sources, aluminum foundries are involved in producing components for wind turbines and solar panels.
Innovations and Technological Advancements:
To remain competitive and meet the demands of various sectors, aluminum foundries are embracing innovations and technological advancements:
a. Lightweighting: The automotive and aerospace industries are pushing for lighter materials, driving the development of advanced aluminum alloys that offer both strength and weight savings.
b. 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing is being explored for producing complex aluminum parts with improved efficiency and reduced waste.
c. Automation: Robotics and automation are streamlining production processes, improving precision, and reducing labor costs.
d. Digital Twin Technology: Digital twin technology allows for real-time monitoring and optimization of manufacturing processes, enhancing overall efficiency.
e. Sustainability Initiatives: Foundries are investing in sustainable practices, such as using recycled aluminum and adopting circular economy principles.
Export Opportunities and Global Impact:
Aluminum foundries have a significant global impact. They export a substantial portion of their products to international markets, particularly North America. The strategic location and trade agreements have facilitated these export opportunities. As global demand for aluminum products continues to rise, foundries are well-positioned to meet these needs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the aluminum foundry industry is a dynamic and growing sector, vital to multiple industries and the country’s economic development. Its strategic location, skilled workforce, and commitment to sustainability have positioned it for further success.
The industry’s future prospects are promising, with opportunities for innovation, diversification, and expansion into emerging markets. By continuing to embrace advanced technologies and sustainable practices, aluminum foundries can secure their role as key players in the global aluminum supply chain.
As the industry evolves, collaboration between government agencies, educational institutions, and the private sector will be crucial in driving innovation and addressing challenges. The aluminum foundry industry is poised to contribute significantly to the country’s industrial growth and competitiveness on the global stage.
If you would like to delve deeper into any specific aspect or have additional questions, please let me know, and I’ll provide further information accordingly.


