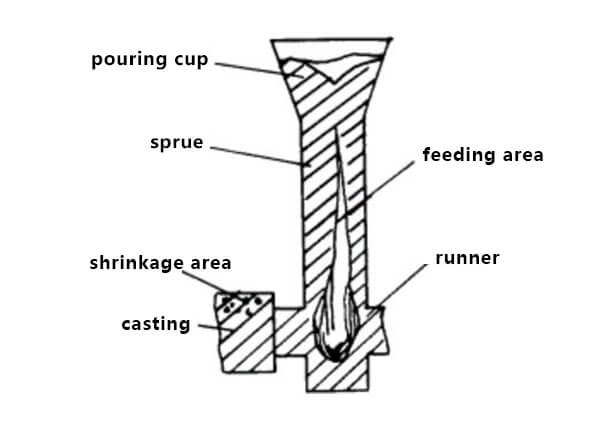
In foundry operations, runners and risers are essential components of the casting process, playing critical roles in ensuring the quality and integrity of the final cast metal product.
Understand the Runner and Riser in Foundry
Runner in Foundry:
- Definition: A runner is a channel or passage that facilitates the flow of molten metal from the pouring basin or sprue to the mold cavities.
- Function: Runners distribute the molten metal evenly to various parts of the mold, allowing for proper filling and ensuring that each cavity receives an adequate amount of metal.
- Importance: Properly designed runners help prevent defects like misruns, cold shuts, and incomplete fillings by controlling the flow of metal within the mold.
Riser in Foundry:
- Definition: A riser, also known as a feeder, is a reservoir of molten metal that provides additional material to compensate for shrinkage as the casting solidifies.
- Function: Risers act as a source of extra molten metal that feeds the casting as it cools and solidifies, helping to prevent shrinkage-related defects like shrinkage cavities and porosity.
- Importance: Risers are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the casting by ensuring that any shrinkage voids are compensated for with additional molten metal.
Overall Significance of Runner and Riser in Foundry:
Quality Assurance: Proper design and implementation of runners and risers are essential for producing high-quality castings free from defects.
Optimization: Foundries often utilize simulation tools to optimize the design of runners and risers to achieve efficient metal flow and feeding during the casting process.
Continuous Improvement: Foundries continuously refine their casting processes, including the design and placement of runners and risers, to enhance efficiency and minimize defects in cast metal products.
Understanding the functions and significance of runners and risers in foundry operations is crucial for achieving optimal casting results and ensuring the production of high-quality metal components.