Introduction
Castings are an important component of modern engineering and manufacturing. They provide a cost-effective solution for the production of complex parts and components that would be more expensive or impossible to produce using other methods. Castings are used in a vast array of industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, energy, and construction, among others. However, casting defects are a common problem that can lead to reduced product quality, increased manufacturing costs, and potential safety hazards. Some of the common casting defects include porosity, shrinkage, cracks, and inclusions, among others. In this paper, we discuss common defects in castings and their solutions using ceramic foam filters.
Porosity
Porosity is a common casting defect that occurs when gas or air bubbles become trapped in the metal during solidification. It can occur due to several reasons, including too high pour temperature, inadequate venting, improper gating, or poor metal quality. Porosity can lead to reduced mechanical strength, decreased corrosion resistance, and increased susceptibility to crack propagation.
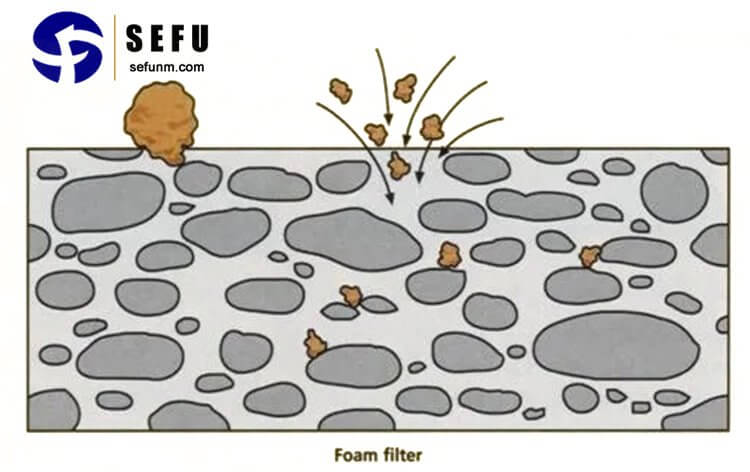
Ceramic foam filters can effectively reduce the porosity in castings by trapping and removing the gas and air bubbles present in the molten metal. They act as a physical barrier that prevents the entry of inclusions and other impurities into the casting. Ceramic foam filters also promote better filling of the mold cavity, thereby reducing the likelihood of porosity formation. They can be used both in gravity-based and pressure-based casting processes to improve the quality of the castings.
Shrinkage
Shrinkage occurs when the volume of the metal decreases during solidification, leading to voids and cracks in the casting. It can occur due to several reasons, including thermal contraction, insufficient feeding, or poor gating. Shrinkage defects can lead to reduced product quality, increased scrap rates, and increased manufacturing costs.
Ceramic foam filters can prevent shrinkage by promoting better flow of the molten metal into the mold cavity. They act as a flow modifier that reduces the turbulence of the metal during casting and ensures that the metal fills the mold cavity uniformly. Ceramic foam filters also increase the solidification rate by promoting rapid cooling of the metal. This reduces the overall shrinkage of the metal and produces a more uniform microstructure.
Cracks
Cracks are a common casting defect that occurs due to various reasons, including thermal stress, shrinkage, or mechanical stress. Cracks can lead to product failure, reduced mechanical strength, and increased scrap rates. They can also lead to safety hazards in critical applications, such as aerospace and medical devices.

Ceramic foam filters can reduce the likelihood of cracks by promoting better feeding and filling of the mold cavity. They ensure that there are no air pockets or voids in the mold, which can lead to stress concentration and crack propagation. Ceramic foam filters also reduce thermal stress by promoting rapid cooling of the metal, thereby reducing the likelihood of thermal cracking.
Inclusions
Inclusions are small particles or impurities that become trapped in the metal during solidification. They can come from various sources, including the furnace, the melting process, or the mold. Inclusions can reduce the mechanical strength, increase the susceptibility to corrosion, and lead to premature failure of the castings.
Ceramic foam filters can prevent the entry of inclusions into the mold cavity by trapping them in the filter. They act as a physical barrier that prevents the impurities from entering the solidifying metal. Ceramic foam filters can also remove any slag or non-metallic particles present in the molten metal, thereby reducing the likelihood of inclusion formation.
Conclusion
Casting defects are a common problem that can lead to reduced product quality, increased manufacturing costs, and potential safety hazards. Some of the common casting defects include porosity, shrinkage, cracks, and inclusions, among others. However, ceramic foam filters can be used to mitigate these defects and improve the quality of the castings. Ceramic foam filters can reduce the porosity by removing trapped gas and air bubbles, prevent shrinkage by promoting better filling and feeding of the mold cavity, reduce the likelihood of cracks formation by preventing stress concentration and thermal stress, and prevent the entry of inclusions by trapping them in the filter. By using ceramic foam filters, manufacturers can produce high-quality castings that meet the required specifications and standards.


