Introduction:
The aviation industry has always been at the forefront of technological innovation. From the design of cutting-edge aircraft to the manufacturing of essential components, precision and quality are paramount. One crucial aspect of aircraft production that often goes unnoticed but is of utmost importance is aviation parts casting. In this article, we will explore the significance of aviation parts casting in America and how technologies like ceramic foam filters are playing a pivotal role in ensuring safety and performance in the skies.
I. The Importance of Aviation Parts Casting
Precision and reliability are non-negotiable in aviation. Every component of an aircraft, whether it’s a turbine blade, engine casing, or landing gear component, must meet stringent quality standards. Casting, as a manufacturing process, has been instrumental in producing complex and durable aviation parts. Here’s why aviation parts casting is indispensable:
1. Complex Geometry: Aviation components often have intricate shapes that cannot be achieved through traditional machining processes alone. Casting allows for the creation of these complex shapes with high precision.
2. Weight Savings: Weight is a critical factor in aviation. Cast parts are often lighter than their forged or machined counterparts, contributing to fuel efficiency and overall performance.
3. Material Selection: Casting provides flexibility in material selection. Aerospace-grade alloys can be precisely cast to meet the specific requirements of each part.
4. Cost-Effective: Mass production of aviation components through casting can be more cost-effective than other manufacturing methods.
II. The Role of Ceramic Foam Filters
Ceramic foam filters are a crucial component in the aviation parts casting process. They are used for filtering molten metal before it enters the mold cavity. Here’s how ceramic foam filters work and why they are indispensable:
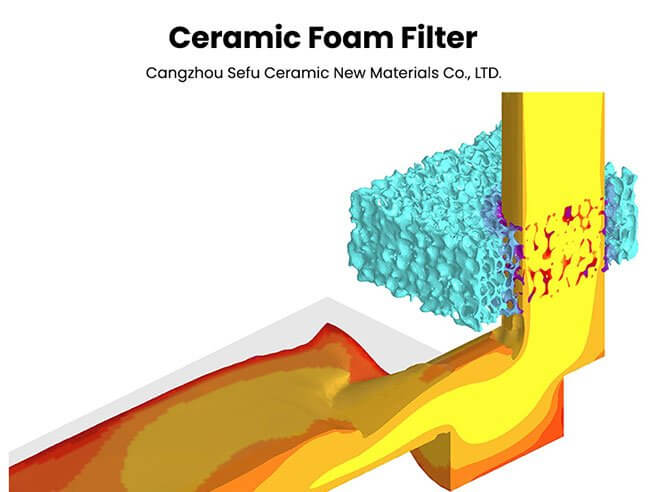
1. Filtration: During casting, impurities and solid particles can be present in the molten metal. Ceramic foam filters act as a barrier, trapping these impurities and ensuring that only clean metal flows into the mold.
2. Improved Quality: By removing impurities, ceramic foam filters help produce aviation parts with superior mechanical properties, reducing the risk of defects that could compromise safety.
3. Heat Insulation: Ceramic foam filters also provide a level of insulation, helping to maintain the temperature of the molten metal as it flows into the mold. This temperature control is critical for achieving the desired properties in the final product.
4. Material Compatibility: Ceramic foam filters are compatible with a wide range of metal alloys commonly used in aviation, including aluminum, titanium, and superalloys.
III. Advancements in Aviation Parts Casting
The aviation industry continually pushes the boundaries of what is possible, and aviation parts casting is no exception. Several advancements have been made in recent years to improve the precision, efficiency, and reliability of casting processes:
1. 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, have found applications in aviation parts casting. They enable the creation of intricate molds and patterns with high precision.
2. Simulation and Modeling: Advanced computer simulations and modeling techniques are used to optimize casting processes. This reduces the need for physical prototypes and minimizes errors.
3. Automation: Robotics and automation have been integrated into casting facilities, streamlining the production process and enhancing consistency.
4. Alloys and Materials: Research into advanced alloys and materials for aviation has led to improved performance and durability in cast parts.
IV. Sustainability in Aviation Casting
In addition to advancements in technology, sustainability has become a key focus in aviation parts casting. With the industry’s growing awareness of environmental concerns, efforts are being made to reduce waste, energy consumption, and emissions in the casting process. This includes recycling and responsible disposal of casting materials, optimizing energy use, and exploring eco-friendly casting techniques.
V. Quality Assurance in Aviation Casting
Quality assurance is paramount in aviation parts casting, and various measures are in place to ensure the highest standards are met:
1. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): NDT techniques such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection are used to identify internal defects in cast parts without causing any damage. This helps in early detection and prevention of potential issues.
2. Material Testing: Rigorous material testing is performed to verify that the alloys used in aviation casting meet specific strength, heat resistance, and fatigue properties required for safe operation.
3. Certification and Compliance: Aviation parts manufacturers adhere to stringent industry standards and certifications, including AS9100 and Nadcap, to ensure compliance with aviation regulations.
4. Traceability: The ability to trace the origin and history of each cast part is crucial. Detailed records are maintained to track the materials, manufacturing processes, and inspections for every component.
VI. Challenges in Aviation Casting
While aviation casting has made significant strides, it faces ongoing challenges:
1. Demand for Lightweight Materials: As aircraft manufacturers seek to reduce fuel consumption, the demand for lightweight materials like carbon composites is increasing. This poses challenges for traditional casting methods, which may need to adapt to accommodate new materials.
2. Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations require casting facilities to minimize emissions, reduce waste, and adopt cleaner production methods.
3. Skilled Workforce: Maintaining a highly skilled workforce capable of operating advanced casting machinery and embracing new technologies is an ongoing challenge.
VII. Future Prospects
The future of aviation parts casting in America is promising, driven by innovation, sustainability, and safety:
1. Advanced Materials: Continued research into advanced materials, including composites, will reshape the landscape of aviation casting.
2. Digital Twins: Digital twin technology will become integral, allowing real-time monitoring and optimization of casting processes.
3. Sustainable Practices: Sustainable casting practices will become the norm, with a focus on reducing environmental impact.
4. Global Collaboration: Collaboration between aviation manufacturers, casting facilities, and research institutions will drive progress and ensure the highest quality standards.
Conclusion
Aviation parts casting in America is an industry vital to the safety and performance of aircraft. It combines tradition with innovation, craftsmanship with technology, and precision with reliability. The role of ceramic foam filters in maintaining the integrity of cast components cannot be overstated, as they contribute to safer and more efficient aviation.
As we look to the future, advancements in materials, technologies, and sustainability practices will continue to shape the industry. The aerospace industry’s commitment to excellence and safety ensures that aviation remains one of humanity’s greatest achievements, and aviation parts casting plays an indispensable role in achieving that goal.
In a world where aviation represents not only progress but also the bridge to new horizons, aviation parts casting will remain a cornerstone of the industry, assuring that every journey begins and ends safely, with precision-crafted components that meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.

