Introduction:
Ceramic foam filter has emerged as critical components in various industrial applications, offering numerous advantages over traditional filtration methods. The unique structures of ceramic foam filters provide enhanced filtration efficiency, improved mechanical strength, and excellent thermal and chemical stability. This essay aims to explore the advantages of the structures of ceramic foam filters, highlighting their impact on industrial processes and the quality of end products.
Section 1: Enhanced Filtration Efficiency
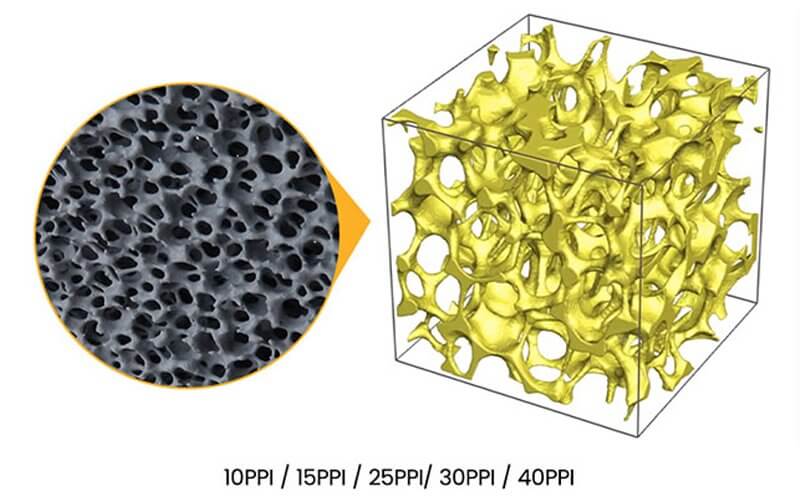
The intricate structure of ceramic foam filters plays a pivotal role in enhancing filtration efficiency. The three-dimensional network of interconnected pores creates an extended filtration surface area, allowing for the effective capture and retention of impurities. This structure ensures that the molten metal passes through a tortuous path, facilitating the entrapment of particles, slag, and other contaminants. As a result, ceramic foam filters provide a high level of filtration effectiveness, leading to cleaner and higher-quality end products.
Section 2: Improved Mechanical Strength
One of the key advantages of ceramic foam filters is their superior mechanical strength compared to conventional filters. The porous structure of these filters consists of a network of struts and nodes that form a robust framework. This design provides excellent structural integrity and resistance to deformation during handling and operation. The enhanced mechanical strength of ceramic foam filters ensures their durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and resulting in cost savings for industrial processes.
Section 3: Thermal and Chemical Stability
Ceramic foam filters exhibit exceptional thermal and chemical stability, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications. The filters are typically composed of high-temperature-resistant ceramic materials such as alumina, zirconia, or silicon carbide. These materials can withstand extreme temperatures without significant structural degradation, maintaining their integrity and filtration efficiency. Additionally, ceramic foam filters are highly resistant to chemical corrosion, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of molten metals and alloys. This stability enables their use in diverse industrial processes involving aggressive or high-temperature environments.
Section 4: Versatility and Customization
Ceramic foam filters offer remarkable versatility and customization options to meet specific industrial requirements. Manufacturers can tailor the pore size, thickness, and density of the filters to suit different applications. This flexibility allows for precise control over the filtration process, optimizing the removal of targeted impurities. Furthermore, ceramic foam filters can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, enabling their integration into different casting systems and industrial setups. This adaptability makes ceramic foam filters suitable for a wide range of industries, including foundries, metal casting, and molten metal filtration processes.
Section 5: Enhanced Flow Control
The unique structure of ceramic foam filters provides an additional advantage in terms of flow control during industrial processes. By carefully selecting the pore size and distribution, manufacturers can regulate the flow rate of molten metal through the filter. This controlled flow prevents turbulence and excessive splashing, reducing the likelihood of re-entrainment of impurities. The enhanced flow control not only improves filtration efficiency but also ensures a smoother casting process, leading to higher-quality end products with minimal defects and better dimensional accuracy.

Section 6: Reduced Casting Defects
Ceramic foam filters significantly contribute to the reduction of casting defects, thereby enhancing the overall quality of the end products. The efficient removal of impurities, such as non-metallic inclusions and oxide particles, minimizes the risk of defects like porosity, surface irregularities, and mechanical weaknesses. By using ceramic foam filters, industrial processes can achieve a higher level of casting integrity, resulting in superior mechanical properties, improved surface finishes, and increased customer satisfaction.
Section 7: Improved Environmental Sustainability
Another notable advantage of ceramic foam filter structures is their positive impact on environmental sustainability. These filters are typically made from non-toxic and recyclable ceramic materials, reducing the environmental impact compared to alternative filtration materials. The large throughput of ceramic foam filters further contributes to sustainability by reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing waste generation. Additionally, the efficient removal of impurities by ceramic foam filters helps reduce the need for excessive post-casting treatments and rework, leading to energy savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
Section 8: Enhanced Productivity and Cost Efficiency
The advantages offered by ceramic foam filter structures translate into improved productivity and cost efficiency for industrial processes. The high filtration efficiency and reduced casting defects result in fewer rejects and rework, saving both time and resources. Moreover, the enhanced mechanical strength and durability of ceramic foam filters reduce the frequency of filter changes, leading to increased operational uptime and cost savings. The customization options and flow control capabilities of ceramic foam filters further contribute to optimized process parameters and streamlined production, ultimately improving overall productivity and profitability.
Section 9: Application Examples
Ceramic foam filters find wide applications across various industries. In the foundry sector, they are extensively used in casting processes for aluminum, steel, and other metals, ensuring the production of high-quality castings. In the metal refining industry, ceramic foam filters play a vital role in the filtration of impurities during the purification of molten metals. Additionally, ceramic foam filters find application in the production of advanced ceramics, where they assist in removing impurities and achieving precise material properties.

Conclusion:
The advantages offered by the structures of ceramic foam filters have revolutionized industrial processes, particularly in foundries, metal casting, and molten metal filtration. Their enhanced filtration efficiency, improved mechanical strength, thermal and chemical stability, versatility, and customization options have significantly impacted the quality of end products, productivity, and cost efficiency. Furthermore, their flow control capabilities and contribution to reduced casting defects have elevated the standards of industrial operations. With their environmental sustainability and positive economic impact, ceramic foam filters continue to be indispensable components in various industries, driving progress and excellence in manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, the structures of ceramic foam filters offer a multitude of advantages that make them highly desirable for industrial applications. Their unique design enhances filtration efficiency, improves mechanical strength, and provides excellent thermal and chemical stability. These filters offer versatility, customization options, and flow control capabilities, resulting in reduced casting defects and improved productivity. Moreover, their positive environmental impact and cost efficiency further strengthen their position as indispensable components in various industrial processes. The ongoing advancements in ceramic foam filter technology continue to propel industries toward higher standards of quality, sustainability, and efficiency.

