Introduction
Clean and safe drinking water is a fundamental necessity for all living beings. However, in many parts of the world, access to uncontaminated water is still a significant challenge. One promising solution to address this issue is the use of ceramic filtration systems. These innovative filtration technologies offer a sustainable and cost-effective approach to purifying water, making it suitable for various applications such as domestic use, industrial processes, and even emergency situations. In this article, we will explore the working principles, advantages, applications, and future prospects of ceramic filtration systems.
I. How Ceramic Filtration Systems Work
Ceramic filtration systems are designed to remove impurities, pathogens, and suspended solids from water through a multi-step process. The core component of these systems is the ceramic filter, which is typically made of porous clay or a blend of clay and other natural materials. Water passes through the tiny pores of the ceramic filter, trapping contaminants while allowing clean water to flow through.
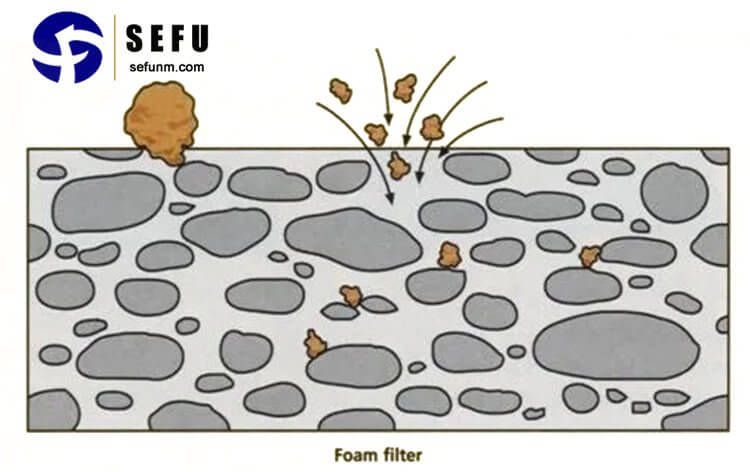
II. Key Advantages of Ceramic Filtration Systems
Cost-effectiveness: Ceramic filters are relatively low-cost compared to other advanced filtration technologies. They are also durable, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Longevity: Properly maintained ceramic filters can last for several years, providing a sustainable solution for clean water access.
Effectiveness: Ceramic filtration systems effectively remove bacteria, protozoa, suspended solids, and other harmful particles, ensuring the water’s safety for consumption.
Eco-friendly: The production and use of ceramic filters have a lower environmental impact compared to chemical water treatment methods.
III. Applications of Ceramic Filtration Systems
Domestic Use: Ceramic filtration systems are suitable for households, especially in rural areas or regions lacking access to centralized water treatment facilities.
Community Water Supply: They can be employed in community-based water supply systems, providing clean water to a larger population.
Disaster Relief: During emergencies and natural disasters, ceramic filtration systems can provide a quick and reliable source of safe drinking water.
Industrial Processes: Ceramic filters find applications in various industries, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment.
IV. Challenges and Improvements
Despite their numerous advantages, ceramic filtration systems also face some challenges. The flow rate of water through ceramic filters can be relatively slow, which can limit their use in high-demand scenarios. Additionally, clogging of the pores may occur over time, reducing the filter’s efficiency.
However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving the performance of ceramic filters. Advancements in filter design, pore size optimization, and antimicrobial treatments are being explored to address these limitations and enhance their overall effectiveness.
V. Future Prospects
The future of ceramic filtration systems looks promising. As technology continues to advance, these filtration systems are expected to become even more efficient, compact, and cost-effective. Integration with smart monitoring and remote management systems will likely enable real-time data monitoring and maintenance, further improving their usability and sustainability.

VI. The Role of Ceramic Filters in Water Purification
Ceramic filters are a vital component of the filtration process, and their effectiveness is attributed to their porous structure. These filters are carefully engineered with controlled pore sizes to trap contaminants while allowing water molecules to pass through. The pores are often on the micron or sub-micron scale, effectively removing harmful particles like bacteria, protozoa, cysts, and sediments.
The filtration mechanism is primarily based on mechanical straining, but it may also involve other processes like adsorption and electrostatic attraction. Some advanced ceramic filters are further enhanced with a silver-based antimicrobial agent, which helps inhibit the growth of bacteria and viruses trapped within the filter, ensuring the long-term safety of the treated water.
VII. Comparative Analysis: Ceramic Filtration vs. Traditional Water Treatment Methods
When comparing ceramic filtration systems to traditional water treatment methods like chlorination or ultraviolet (UV) treatment, several key advantages emerge:
Sustainability: Ceramic filtration systems require minimal energy input, making them more environmentally friendly and sustainable compared to energy-intensive treatment processes like UV disinfection or reverse osmosis.
Cost-effectiveness: As mentioned earlier, ceramic filters are relatively inexpensive to produce and maintain, making them economically viable, especially in resource-constrained regions.
In Dependence from Chemicals: Unlike chemical-based treatment methods, ceramic filtration systems do not rely on the use of chemicals, which can sometimes introduce unwanted byproducts or taste in the treated water.
Robustness: Ceramic filters are resistant to physical wear and tear, making them well-suited for challenging environments and prolonged use.
VIII. Global Impact and Humanitarian Use
Ceramic filtration systems have made a significant impact on humanitarian efforts and emergency response situations. During natural disasters, conflicts, or refugee crises, access to clean drinking water becomes a critical concern. Ceramic filters, with their simplicity, durability, and effectiveness, have played a pivotal role in providing safe water to affected communities and saving countless lives.
Moreover, in regions where access to potable water is scarce or unreliable, ceramic filtration systems have been deployed in community-led water projects. Non-governmental organizations and local communities have embraced these systems due to their ease of use and maintenance, fostering greater ownership and sustainability of water supply initiatives.
IX. Future Research and Advancements
The field of ceramic filtration is continuously evolving, with researchers and engineers exploring novel approaches to enhance filter performance, flow rates, and overall efficiency. Ongoing research focuses on refining the manufacturing process to optimize pore size distribution, reducing clogging issues, and improving filtration rates.
In addition, efforts are being made to explore ceramic materials with enhanced adsorption capabilities to target specific pollutants like heavy metals and organic contaminants.
Collaborations between academia, industry, and non-profit organizations are fostering innovation in ceramic filtration technology, with the ultimate goal of providing clean water solutions to even more communities around the world.
Addressing Challenges: Flow Rate and Clogging
One of the primary challenges faced by ceramic filtration systems is the relatively slow flow rate of water through the filters. This limitation can be a hindrance, especially in areas with high water demand. However, researchers are actively working to optimize the flow rates without compromising filtration efficiency.
To address clogging issues, engineers are exploring pre-treatment techniques that can help reduce the amount of suspended solids and debris reaching the ceramic filters. Additionally, regular maintenance practices, such as brushing or scrubbing the filter surface, can help extend its lifespan and prevent clogging.
X. Integrating Ceramic Filtration with Water Distribution Networks
As ceramic filtration gains popularity, efforts are being made to integrate these systems into existing water distribution networks. This involves designing ceramic filter units that can be connected to pipes, taps, and reservoirs to facilitate the distribution of treated water to communities or industries. These integrated systems aim to ensure a continuous and reliable supply of clean water.
XI. Promoting Awareness and Education
While ceramic filtration systems offer a practical and cost-effective solution, their successful implementation relies on raising awareness and educating communities about their benefits and proper usage. Initiatives focused on promoting the importance of clean water, sanitation practices, and the significance of maintaining and regularly replacing ceramic filters can help ensure the long-term success of these systems.
XII. Scaling up for Global Impact
To have a meaningful global impact, it is essential to scale up the production, distribution, and accessibility of ceramic filtration systems. Collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, private enterprises, and research institutions can help streamline production processes, reduce costs, and expand the reach of these systems to the most vulnerable regions.
XIII. Complementary Water Treatment Technologies
Ceramic filtration systems can also be integrated with other water treatment technologies to address specific challenges. For instance, combining ceramic filtration with activated carbon filters can effectively remove a broader range of contaminants, including organic pollutants and some chemical compounds. Such integrated approaches can offer comprehensive water treatment solutions tailored to diverse water quality conditions.
XIV. Supporting Local Manufacturing and Entrepreneurship
Encouraging local production of ceramic filters not only stimulates local economies but also ensures a sustainable supply chain. Supporting local entrepreneurs to manufacture, distribute, and maintain these filters empowers communities to take charge of their water supply needs and fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
Conclusion:
Ceramic filtration systems have emerged as a viable, sustainable, and life-changing solution for accessing clean water in various regions around the world. Despite some challenges, the benefits of these systems far outweigh their limitations. As global water scarcity continues to be a pressing concern, the continuous development and widespread adoption of ceramic filtration systems are crucial for achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal of universal access to safe and clean drinking water.
By combining technological advancements, awareness campaigns, and community engagement, ceramic filtration can pave the way toward a future where clean water is no longer a privilege but a fundamental right for every individual on the planet.


