In iron casting operations, gating system design directly determines casting quality, yield rate, and overall production efficiency. A well-designed system ensures smooth mold filling, controlled solidification, and minimal defects. As foundries continue optimizing both sustainability and cost performance, paper casting runners are becoming an increasingly important component in modern gating strategies.
When applied correctly in iron casting processes such as lost foam casting (EPC) and traditional sand casting, paper casting runners enable foundries to improve yield, reduce excess metal consumption, and streamline production workflows.
This article explores how to design efficient gating systems using paper casting runners—focusing on engineering principles, performance optimization, and practical implementation in iron foundries.
The Importance of Gating System Design in Iron Casting
A gating system typically consists of:
-
Sprue
-
Runner
-
Ingate
-
Riser
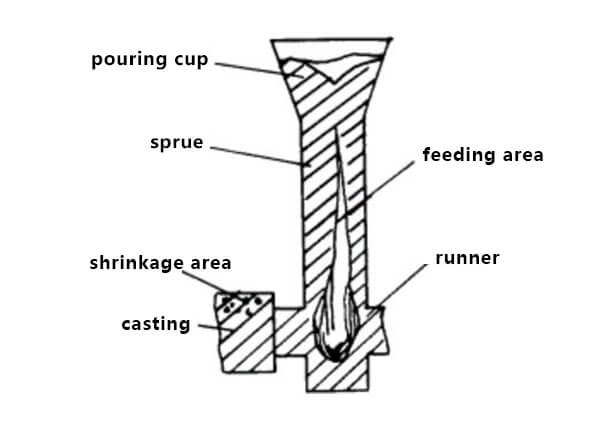
Its purpose is to transport molten iron from the pouring basin into the mold cavity in a controlled and stable manner. Poor gating design can result in:
-
Turbulence
-
Air entrapment
-
Cold shuts
-
Misruns
-
Shrinkage defects
-
Low casting yield
Because iron casting involves high pouring temperatures and significant metal mass, flow control and directional solidification are critical.
Paper casting runners offer an opportunity to redesign traditional gating systems with improved efficiency and material optimization.
What Makes Paper Casting Runners Suitable for Iron Casting?
Paper casting runners are pre-formed, heat-resistant paper-based components engineered specifically for iron casting applications. They are suitable for:
-
Gray iron casting
-
Ductile iron casting
-
Lost foam casting systems
-
Traditional sand casting and green sand molding
Their lightweight structure and engineered thermal properties make them ideal for optimizing runner geometry while minimizing unnecessary metal mass.
Core Design Principles for Efficient Gating Systems
Control of Metal Flow Velocity
An efficient gating system must control molten iron velocity to prevent turbulence. Excessive turbulence can cause:
-
Oxide formation
-
Gas entrapment
-
Surface defects
When designing gating systems with paper casting runners:
-
Optimize runner cross-sectional area
-
Maintain smooth transitions between sprue, runner, and ingates
-
Avoid abrupt directional changes
Paper runners allow precise dimensional control, making it easier to fine-tune flow velocity compared to bulk metal runner systems.

Optimizing Runner Cross-Section Geometry
The cross-sectional shape of the runner significantly influences flow characteristics.
Common design considerations include:
-
Trapezoidal or rectangular cross-sections for stability
-
Balanced gating ratios
-
Proper choke area positioning
With paper casting runners, foundries can achieve consistent geometry and repeatable results, helping improve process stability in both lost foam and sand casting operations.
Maximizing Casting Yield
Yield improvement is one of the main advantages of using paper casting runners.
Traditional metal runners solidify with the casting and require removal and remelting. This increases:
-
Energy consumption
-
Furnace load
-
Labor costs
By reducing unnecessary metal mass in the runner system, paper casting runners help:
-
Increase yield percentage
-
Reduce remelting volume
-
Improve overall material efficiency
Higher yield directly translates into lower production costs and improved sustainability metrics.
Designing for Directional Solidification
Efficient gating design must promote directional solidification—from the casting extremities toward the riser.
Key considerations include:
-
Proper ingate placement
-
Controlled metal temperature distribution
-
Balanced filling pattern
Paper casting runners contribute by enabling streamlined gating layouts that minimize excess metal volume while maintaining proper feeding paths.

Integration with Lost Foam Casting (EPC)
In lost foam casting, gating system performance is closely tied to foam pattern vaporization behavior.
When designing gating systems with paper casting runners in EPC:
-
Ensure smooth and stable iron flow
-
Prevent excessive pressure buildup
-
Maintain consistent filling rates
Paper runners integrate well with lost foam systems due to their lightweight structure and compatibility with iron pouring conditions. They also help simplify gating assembly, improving production efficiency.
Enhancing Sand Casting Efficiency
In traditional sand casting:
-
Mold filling stability is critical
-
Cleaning and finishing labor significantly affect costs
Paper casting runners help reduce:
-
Excess runner metal attached to castings
-
Grinding and fettling time
-
Post-processing labor
This results in faster turnaround times and improved production flow.
Practical Engineering Considerations
When implementing paper casting runners into gating system design, foundries should evaluate:
Structural Integrity: The runner must withstand molten iron pressure without deformation.
Thermal Resistance: Paper materials must be engineered to tolerate iron pouring temperatures.
Mold Compatibility: The runner must fit securely within sand molds or lost foam assemblies.
Production Volume: Runner design may vary depending on batch size and casting weight.
Proper engineering validation and testing are recommended before full-scale implementation.
Economic and Sustainability Benefits
Efficient gating systems designed with paper casting runners contribute to:
-
Reduced metal waste
-
Lower melting energy requirements
-
Improved carbon efficiency
-
Simplified handling and installation
-
Reduced finishing labor
For high-volume iron foundries, even small improvements in yield and labor efficiency can result in substantial annual cost savings.
As environmental regulations tighten and energy costs rise, optimizing the gating system becomes a strategic investment rather than a minor process adjustment.
Common Design Mistakes to Avoid
When adopting paper casting runners, avoid:
-
Oversized runner cross-sections that reduce yield
-
Poor gating ratios leading to turbulence
-
Inadequate structural support in heavy iron castings
-
Applying the system outside its intended iron casting scope
Clear understanding of application boundaries ensures reliable performance.
The Future of Efficient Gating Design
Modern foundries are increasingly focused on lean manufacturing principles:
-
Minimize waste
-
Maximize yield
-
Reduce energy consumption
-
Improve workflow efficiency
Gating system design plays a critical role in achieving these goals.
Paper casting runners represent a practical innovation that aligns with modern iron casting priorities—especially in lost foam casting and traditional sand casting environments.
Conclusion
Designing efficient gating systems with paper casting runners requires a combination of sound engineering principles and process optimization. When properly implemented in iron casting operations, they offer:
-
Improved yield
-
Reduced remelting
-
Enhanced mold filling control
-
Lower labor and finishing costs
-
Stronger sustainability performance
For foundries seeking to enhance competitiveness while reducing environmental impact, optimizing gating design with paper casting runners is a forward-thinking and results-driven solution.

