In casting production, slag inclusion defects are one of the common quality problems. When facing the problem of slag inclusion, many casting engineers will first ask: “Is there a filter?” However, simply placing a filter cannot completely solve the problem, especially for large castings, the selection, installation and use of the filter is crucial.
This article will systematically analyze the selection principles, installation techniques and usage precautions of casting filters to help casting practitioners use filters more efficiently to improve the quality of castings.
Types and selection points of casting filters
1. Classification by shape
Straight hole ceramic filter: simple structure, general filtering effect, suitable for scenes with low requirements.
Foam ceramic filter (recommended): has a three-dimensional mesh structure, better filtering effect, can effectively intercept slag and improve the flow state of molten metal.
2. Classification by material
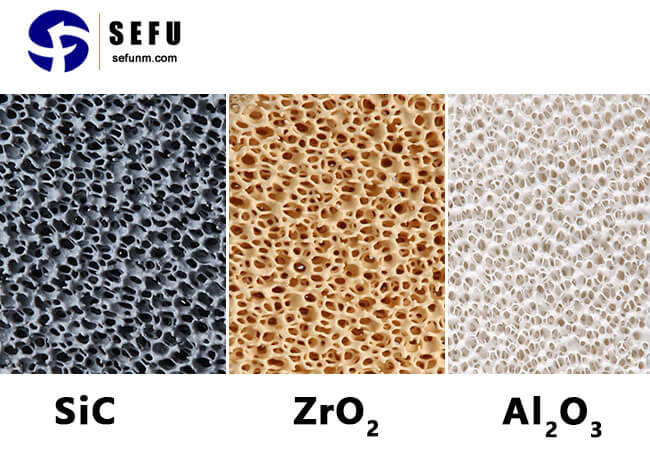
Ceramic Filters of different materials are suitable for different casting conditions:
- Alumina: suitable for cast aluminum, good high temperature resistance.
- Silicon carbide: suitable for cast iron, high temperature resistance, strong thermal shock resistance.
- Zirconia: suitable for ultra-high melting point metals, such as titanium alloys and high temperature alloys.
Key parameters for selection:
- Casting material (gray iron, ductile iron, cast steel, etc.)
- Pouring temperature (filter plate needs to withstand high temperature)
- Metal liquid flow (avoid filter plate clogging or overload)
3. Select by pore size (PPI)
Ductile iron castings: 10~15 PPI is recommended (slightly larger pore size to avoid premature clogging).
Gray iron castings: 10~20 PPI is recommended (pore size can be slightly smaller because the amount of gray iron slag is less).
Calculation of filter capacity
The carrying capacity of the filter plate directly affects its use effect, and the size needs to be reasonably selected according to the metal liquid flow::
- Gray iron castings: 4~6 kg of molten iron can be filtered for every 1 cm² filter area (it is recommended to calculate conservatively based on 4 kg).
- Ductile iron castings: 2~4 kg of molten iron can be filtered for every 1 cm² of filter area (2 kg is recommended).
Calculation formula:
Required filter area=Total casting weight (kg)/Unit filter capacity (kg/cm²)
For example, to cast 100 kg of ductile iron castings, at least 50 cm² of filter area is required (100 ÷ 2 = 50).
Installation position and techniques of ceramic casting filters
Position selection
- As close to the cavity as possible: The closer the filter plate is to the casting, the better the filtering effect.
- Avoid direct impact of molten metal: If it cannot be avoided, the pouring height should be ≤ 300 mm to prevent the filter plate from breaking.
Casting system design
- Open casting system (recommended): The filter plate works best in this system.
- Closed casting system: Try to avoid using casting filters, otherwise it will easily lead to poor flow of molten metal.

Effective molten metal filtration area requirements
The total effective filtration area of the ceramic casting filter should meet the following requirements:
Total filtration area>(2∼5)×blocking cross-sectional area
For example, if the blocking cross-sectional area is 10 cm², the total area of the ceramic filter should be at least 20~50 cm².
Common misunderstandings in using ceramic casting filters
- “Ceramic Filters can completely eliminate slag inclusions”
Filters can reduce slag inclusions, but cannot intercept all impurities 100%, and require good smelting and casting processes.
2. “Filters can be placed anywhere”
Wrong installation position (such as away from the cavity or directly impacted by molten metal) will greatly reduce the filtering effect.
3. “The smaller the aperture, the better”
If the aperture is too small, it is easy to be blocked, especially for ductile iron casting, and a suitable PPI value needs to be selected.
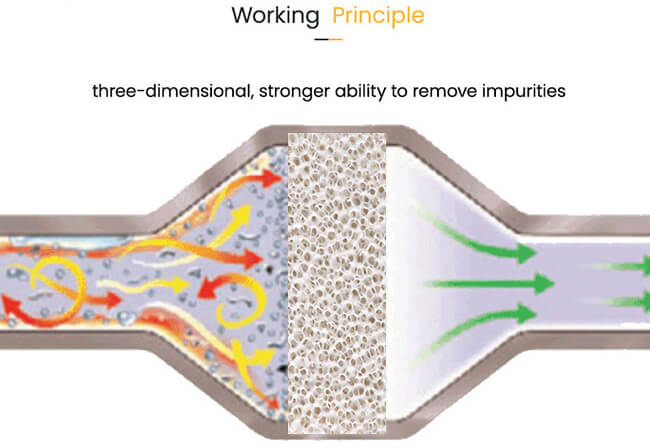
Additional functions of the filter: improving the flow state of molten metal
In addition to filtering impurities, another major function of the filter is:
Converting turbulent molten metal into horizontal flow, reducing oxidation slag and air entrainment, and improving the density of castings.
Summary: Key points for using casting filters
✅ Choose the right type: Foam ceramic filters are preferred, matching casting requirements according to material and pore size.
✅ Calculate the area accurately: Ensure sufficient filtering capacity to avoid blockage or overload.
✅ Reasonable installation: Close to the cavity to avoid direct impact, open casting system is better.
✅ Correct understanding: The ceramic casting filter is an auxiliary means and needs to be combined with good smelting and casting processes.
Final suggestion:
- Check whether the ceramic casting filter is cracked or damp before use.
- The porosity of ceramic filters from different manufacturers varies greatly (40%~90%), and the design needs to be adjusted according to the actual product.
Through scientific selection and correct installation of casting filters, the slag inclusion defects of castings can be significantly reduced and the casting quality can be improved!


