The casting industry is a vital component of global manufacturing, responsible for producing a wide range of products from automobile parts to aerospace components. It plays a crucial role in shaping various industries, and its distribution around the world is indicative of the ever-changing landscape of manufacturing. This article explores the distribution of the casting industry worldwide and delves into the essential role played by ceramic foam filters in enhancing casting quality.
Casting Industry Distribution Around the World:
North America:
In North America, the casting industry has a significant presence, with the United States and Canada being key players.
The automotive and aerospace sectors drive demand for high-quality cast parts.
Europe:
Europe boasts a robust casting industry, with countries like Germany, Italy, and France leading the way.
Precision casting techniques are highly prevalent in Europe, catering to various industries.
Asia:
Asia, particularly China, and India, is known for its extensive casting production.
Low-cost manufacturing and rapid industrialization have made Asian countries major contributors to global casting.
South America:
South American nations, like Brazil and Mexico, have growing casting industries due to their burgeoning automotive and infrastructure sectors.
Ceramic Foam Filters: The Quality Enhancers:
What Are Ceramic Foam Filters?
Ceramic foam filters are porous structures made from ceramic materials.
They are used in the casting industry to remove impurities and improve the quality of molten metal.
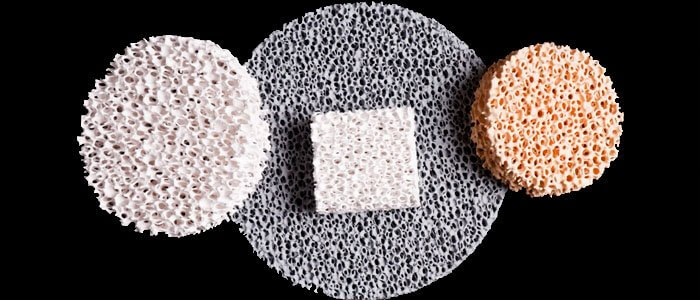
Role of Ceramic Foam Filters in Casting:
Filtration: Ceramic foam filters act as effective filters, removing unwanted impurities like slag and non-metallic inclusions from molten metal.
Heat Insulation: These filters help regulate the temperature of molten metal, ensuring consistent casting quality.
Reduced Porosity: Ceramic foam filters reduce casting defects such as porosity, resulting in stronger and more reliable castings.
Applications of Ceramic Foam Filters:
Automotive Industry:
Ceramic foam filters are widely used in the automotive sector to enhance the quality of engine components like cylinder heads and blocks.
Aerospace Industry:
The aerospace industry relies on ceramic foam filters to ensure the integrity of critical components, such as turbine blades and aircraft structural parts.
Foundries:
Foundries across the globe employ ceramic foam filters to meet stringent quality standards and customer requirements.
Advancements in Ceramic Foam Filter Technology:
Improved Porosity Control:
Recent advancements in manufacturing techniques allow for precise control over the porosity of ceramic foam filters, catering to specific casting requirements.
Customization:
Manufacturers can now customize ceramic foam filters to match the alloy and casting process, optimizing results.
Durability:
Enhanced durability and longevity make ceramic foam filters cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Certainly, let’s delve deeper into some of the key aspects of the casting industry and the pivotal role that ceramic foam filters play:
Challenges and Innovations in the Casting Industry:
Environmental Concerns:
The casting industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint. Efforts are being made to develop more sustainable casting practices, including recycling and waste reduction.
Industry 4.0 Integration:
Industry 4.0 technologies, such as automation, data analytics, and IoT sensors, are transforming the casting industry. They enable real-time monitoring and control of casting processes for improved efficiency and quality.
Alloy Development:
Innovations in metallurgy are leading to the creation of new alloys with enhanced properties. Ceramic foam filters are crucial in maintaining the purity of these alloys during casting.
Regional Highlights:
North America:
The United States, with its advanced aerospace and automotive sectors, relies heavily on casting for critical components.
Investment in research and development contributes to the continuous improvement of casting processes and materials.
Europe:
European foundries often specialize in high-precision casting for luxury goods, industrial equipment, and automotive components.
Sustainable casting practices, including the use of ceramic foam filters, are gaining traction.
Asia:
China’s dominance in global casting production is well-known. The country’s focus on mass production and exportation has driven innovation in casting technology.
India is emerging as a significant player in casting, particularly for automotive and infrastructure projects.
South America:
South American foundries benefit from their proximity to key raw materials. Brazil, in particular, is a major player in the casting of iron and steel products.
VII. Future Trends and Outlook:
Sustainable Practices:
The casting industry will continue to adopt sustainable practices, including recycling scrap metal and implementing eco-friendly casting processes.
3D Printing in Casting:
Additive manufacturing, especially 3D printing, is gaining ground in casting. It offers design flexibility and the ability to create complex geometries while utilizing ceramic foam filters for quality control.
Global Supply Chain Resilience:
Recent disruptions in global supply chains have highlighted the need for greater resilience. The casting industry is likely to see more localized production to mitigate risks.
Research and Development:
Ongoing R&D efforts will lead to the development of advanced ceramic foam filter materials and techniques for even better metal filtration and casting quality.
VIII. Quality Assurance in Casting:
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Quality control is paramount in the casting industry. Non-destructive testing methods such as X-ray, ultrasonic testing, and magnetic particle inspection are used to detect defects in castings.
Simulation Software:
Advanced computer simulation software is employed to optimize casting processes. This helps foundries identify potential defects and improve casting designs before actual production.
IX. Ceramic Foam Filter Varieties:
Different Materials:
Ceramic foam filters are available in various materials like silicon carbide, alumina, and zirconia, each with specific properties suited for different casting applications.
Pore Size Options:
Filters come in a range of pore sizes to match the size of impurities expected in the molten metal. This customization ensures efficient filtration.
X. Training and Skilled Workforce:
Skilled Labor:
The casting industry relies on a skilled workforce that understands the intricacies of casting processes and the proper use of tools like ceramic foam filters.
Training Programs:
Many countries invest in vocational training programs to ensure a steady supply of skilled workers for the casting industry.
XI. The Role of Research Institutions:
Collaborative Research:
Research institutions and universities often collaborate with the casting industry to develop new materials, techniques, and sustainable practices.
Knowledge Transfer:
Research findings are shared with foundries, helping them stay updated with the latest advancements, including those related to ceramic foam filters.
Conclusion:
The casting industry’s dynamic nature, driven by technological advancements and the pursuit of quality, makes it a critical player in global manufacturing. Ceramic foam filters stand as a symbol of the industry’s commitment to producing high-quality castings. Through continuous innovation, skilled workforces, and global collaborations, the casting industry is well-positioned to meet the evolving demands of various sectors while minimizing its environmental impact.

